Embark on a journey through the realm of Strategic management in financial services, where the intricate dance of financial strategies unfolds before your eyes, offering insight and depth into the world of financial services.
Delve deeper into the nuances of strategic planning, competitive analysis, and risk management strategies that form the backbone of success in the financial sector.
Overview of Strategic Management in Financial Services

Strategic management in financial services involves the formulation and implementation of long-term goals and initiatives to achieve competitive advantage and sustainable growth within the financial sector. It entails analyzing the external environment, setting objectives, formulating strategies, and monitoring performance to ensure the organization’s success.
Define Strategic Management in Financial Services
Strategic management in financial services refers to the process of identifying opportunities and threats in the financial industry, setting goals and objectives, formulating strategies to achieve them, and allocating resources effectively to maximize financial performance and competitive advantage.
Importance of Strategic Management in the Financial Sector
Strategic management is crucial in the financial sector as it helps organizations adapt to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements. By aligning their resources with their long-term goals, financial institutions can enhance their competitiveness, improve operational efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth.
Key Components of Strategic Management in Financial Services
- Environmental Analysis: Conducting a thorough analysis of the external environment, including market trends, competition, regulatory changes, and economic conditions, to identify opportunities and threats.
- Goal Setting: Establishing clear and measurable goals and objectives that align with the organization’s mission and vision, ensuring a sense of direction and purpose.
- Strategy Formulation: Developing strategic initiatives and action plans to achieve the set goals, considering factors such as risk management, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
- Resource Allocation: Allocating financial, human, and technological resources effectively to support the implementation of strategic initiatives and maximize performance.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitoring and evaluating the organization’s performance against the set goals, making adjustments as needed to ensure progress towards strategic objectives.
Strategic Planning in Financial Services
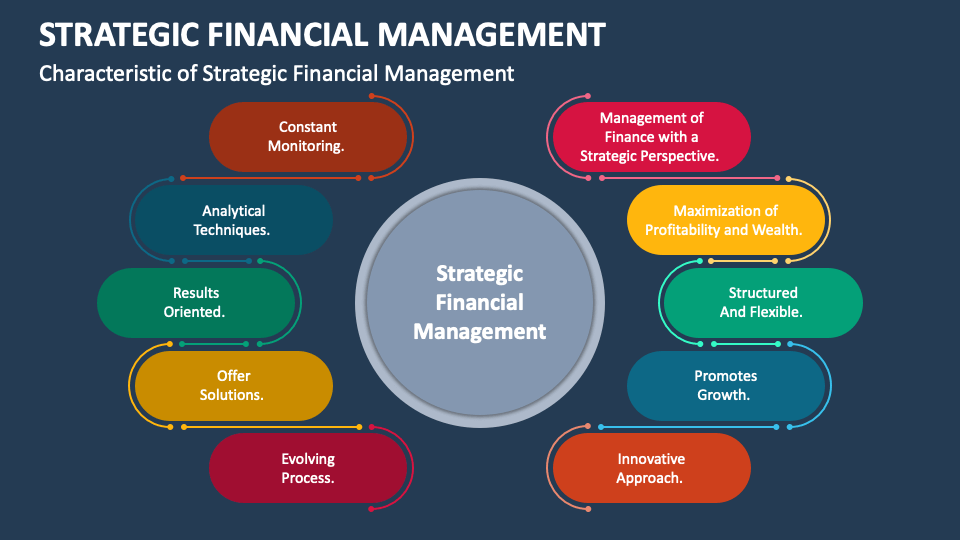
Strategic planning in financial services involves the process of defining an organization’s strategy, setting goals, and outlining the steps needed to achieve those goals. It is a crucial aspect of management in the financial industry as it helps institutions navigate the complex and ever-changing landscape of the market.
Examples of Strategic Planning Tools
- SWOT Analysis: This tool helps financial institutions identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, allowing them to develop strategies that leverage their strengths and address weaknesses.
- PESTLE Analysis: This framework helps in analyzing the external factors that can impact a financial institution, including political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors.
- Balanced Scorecard: This tool enables organizations to align their strategic objectives with key performance indicators in areas such as financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal processes, and learning and growth.
How Strategic Planning Helps Achieve Long-term Goals
Strategic planning helps financial institutions achieve their long-term goals by providing a roadmap for success. By clearly defining objectives, strategies, and action plans, organizations can align their resources and efforts towards a common vision. It allows them to adapt to changes in the market, anticipate risks, and capitalize on opportunities, ultimately leading to sustainable growth and competitiveness in the financial services sector.
Competitive Analysis in Financial Services

The role of competitive analysis in strategic management for financial services is crucial in understanding the competitive landscape, identifying opportunities, and mitigating risks. By evaluating competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, financial institutions can make informed decisions to gain a competitive advantage.
Different Approaches to Competitive Analysis
- Traditional Approach: Involves analyzing competitors’ financial performance, market share, product offerings, and customer base to assess their competitive position.
- SWOT Analysis: Examines competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to identify areas for improvement and potential risks.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Focuses on analyzing the competitive forces within the industry, including the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products or services.
Key Competitors in the Financial Services Industry
- Bank of America: One of the largest financial institutions in the US, focusing on retail banking, wealth management, and investment banking. Their strategy includes a strong focus on digital banking and customer experience.
- JPMorgan Chase: A global financial services firm offering a wide range of products and services, including consumer banking, asset management, and investment banking. Their strategy includes diversification and innovation in financial products.
- Wells Fargo: A diversified financial services company providing banking, insurance, investment, mortgage, and consumer finance services. Their strategy includes a focus on cross-selling and customer relationships.
Risk Management Strategies in Financial Services
Risk management plays a crucial role in the strategic decision-making process for financial services. It helps financial institutions identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks that could impact their operations, financial stability, and reputation. By implementing effective risk management strategies, organizations can protect themselves from uncertainties and make informed decisions to achieve their objectives.
Types of Risk Management Strategies
- Asset Liability Management: This strategy involves managing the assets and liabilities of a financial institution to ensure a balance between risk and return. It helps in optimizing the use of funds and managing interest rate risk.
- Credit Risk Management: Financial institutions assess and manage credit risk by evaluating the creditworthiness of borrowers, setting credit limits, and monitoring loan portfolios. This strategy helps in minimizing the risk of default and loan losses.
- Operational Risk Management: This strategy focuses on identifying and mitigating risks related to internal processes, systems, and human errors. It involves implementing controls, policies, and procedures to prevent operational failures.
- Market Risk Management: Financial institutions manage market risk by monitoring and hedging against fluctuations in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and other market variables. This strategy helps in protecting the institution from adverse market movements.
Impact of Risk Management on Strategic Planning
Risk management has a significant influence on strategic planning in the financial sector. By incorporating risk management into their strategic decision-making process, organizations can make more informed choices, set realistic objectives, and allocate resources effectively. For example, a bank that identifies and mitigates credit risk through robust risk management practices can confidently expand its lending portfolio and pursue growth opportunities without compromising financial stability.
Outcome Summary
As we conclude our exploration of Strategic management in financial services, we reflect on the crucial role strategic management plays in steering financial institutions towards their objectives, paving the way for sustained growth and success in a dynamic industry landscape.